Introduction
On February 12th, 2024, Google implemented a major change in Google Analytics 4 (GA4): the removal of Google Signals from the reporting identity. This decision carries significant implications for how businesses track user behavior and analyze data. In this article, we’ll delve into the essence of Google Signals, its previous role in GA4, and the key impacts and considerations arising from its removal.
Understanding Google Signals
Imagine a user seamlessly browsing your website on their phone, then completing a purchase on their laptop. Google Signals, previously available in GA4, offered a glimpse into this unified user journey. It leveraged anonymized data from signed-in Google users to enhance insights into user demographics (age, gender, interests), cross-device tracking, and audience management for linked Google Ads accounts. Essentially, it painted a more complete picture of user behavior across platforms.
The Role of Reporting Identity
Think of the reporting identity as the glue that binds user data within GA4. By consolidating information from various sources, it grants marketers a holistic view of user interactions. Google Signals, when integrated into this identity, acted as a valuable layer of information from signed-in Google users, enriching the overall data analysis.
Configuration and Benefits
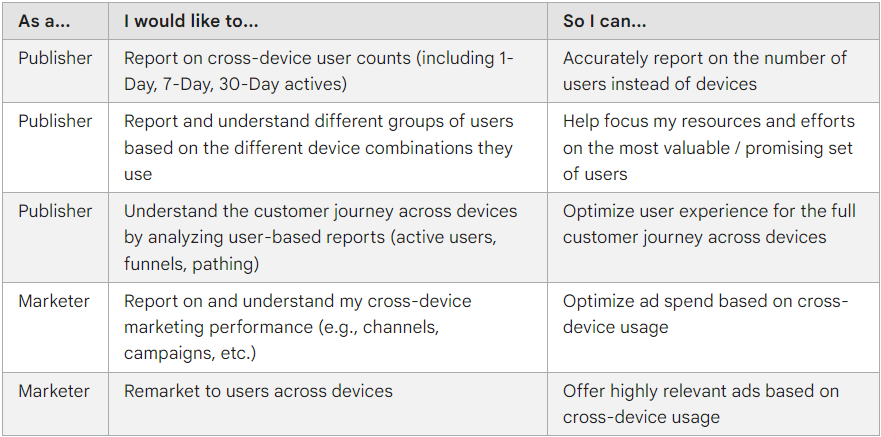
It’s crucial to configure Google Signals to harness its full potential. The benefits of activating Google Signals include:
- Enhanced Cross-Platform Reporting: By integrating User-ID or Google Signals data, marketers can gain insights into user behavior throughout the conversion process, providing a holistic view of the customer journey across various devices and platforms.
- Accurate User Counts: Google Signals helps in refining user counts in reporting by utilizing cross-platform audience criteria, especially for users lacking a User-ID.
- Remarketing Capabilities: Activation of Google Signals allows for the creation of remarketing audiences based on Google Analytics data, facilitating targeted ad campaigns across devices for users with Ads Personalization turned on.
- Demographics and Interests Reporting: Google Analytics can gather additional information on user demographics and interests through device identifiers and data from signed-in users, enriching the dataset available for analysis.
Read more: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/9445345
Considerations and Compliance
- Unsupported Devices: Google Signals does not support tracking on iOS 14+ devices due to Apple’s privacy updates. For these devices, User-ID tracking remains necessary for cross-device analysis.
- Data Retention: Google-signed in data expires after 26 months or according to the Analytics Data Retention settings if they specify a shorter period, ensuring compliance with data privacy standards.
- Data Sharing: The data collected under Google Signals is used exclusively to enhance Google Analytics services, with additional sharing options available through Data Sharing settings or by linking with other Google products.
Impact of Removing Google Signals
Cross-Device Tracking Challenges
While the absence of Google Signals might pose challenges in tracking users across different devices, the impact won’t be universal. Large enterprises heavily reliant on cross-device insights may feel the pinch more acutely. For smaller companies or those with limited adoption of signed-in Google user data, the impact might be negligible.
Reduced Data Thresholds
Previously, Google Signals’ presence triggered data thresholds, potentially limiting data visibility in reports. With its removal, these thresholds are expected to decrease, potentially leading to more complete data sets in GA4, offering a clearer picture of user behaviour.
Adapting to New Reporting Identities
GA4 offers various reporting identities, each with its strengths and limitations. Understanding these options and choosing the right one (Blended, Observed, Device Only) becomes even more crucial in the absence of Google Signals. Consider consulting with data analytics experts to navigate this aspect effectively.
Preparing for the Change
Assess the Impact
Don’t wait for February 12th! Proactively disable the “Include Google Signals in reporting identity” setting in your GA4 properties. This allows you to preview the impact on your reports and assess how significantly it affects your data analysis.
Explore Alternative Data Collection Methods
While Google Signals is gone, explore alternatives like User ID (consent-based) or data modeling to bridge the gap and gather valuable user insights.
Re-evaluate Audience Strategy
Adapting your audience strategy might be necessary. Consider focusing on other segmentation methods like interests or purchase behavior to maintain effective targeting capabilities.
Prioritize User Privacy
Remember, even without Google Signals, data privacy remains paramount. Ensure your privacy policy reflects your data collection practices and that you obtain clear user consent where required.
Future of Google Signals
With the removal of Google Signals from the reporting identity in 2024, GA4 users will need to reassess their analytics and reporting strategies to adapt to the new landscape. This change underscores the evolving nature of digital analytics, emphasizing the importance of flexibility and compliance in data collection and analysis practices.
The removal of Google Signals from the reporting identity signifies a shift in data collection and analysis within GA4. While challenges exist, particularly in cross-device tracking, this change also presents opportunities for more complete data sets and a renewed focus on user privacy. By understanding the impact, exploring alternatives, and adapting your strategies, businesses can continue to leverage GA4 for effective data analysis and marketing success.
